
Healthcare providers are under greater pressure than ever before and are forced to manage various competing demands for their time and attention. As the transition to value-based care accelerates, so does the need to collaborate with health plans to ensure complete, accurate coding and documentation to inform better risk adjustment and for Primary Care Physicians (PCPs) to actively identify and close care gaps. Patients also want (and deserve) quality healthcare interactions that recognize their unique needs, conditions and circumstances.
Against this backdrop, a lot is riding on the annual patient visit. Amid packed schedules, PCPs need to assess risk, address HEDIS gaps and ensure their patient is properly heard and cared for, with all questions answered and concerns addressed.
At the same time, PCPs are chronically short on time and resources needed to complete required coding and documentation—often putting in two extra hours a day just to get through EMR backlogs. The continued rollout of CMS-HCC Model V28 will require even greater coding expertise and scrutiny, a troubling proposition for already-strapped providers who are facing burnout at alarming rates.
Fortunately, by prioritizing and embracing accurate diagnosis coding—and drawing on expert partners like Vatica Health to help upskill PCPs and relieve the admin burden—providers can better identify and manage patient risks, close gaps in care, stay in compliance with evolving guidelines and, ultimately, thrive in a value-based care world.
Putting PCPs at the center of risk adjustment
General Physician, PC, one of the largest and most respected medical groups serving Western New York and Northern Pennsylvania, has made it their mission to deliver quality care that’s second to none. Vatica partners with General Physician, PC to overcome the mounting complexity of risk adjustment and lessen the load associated with coding and documentation.
At the 2024 RISE Conference, Richard Charles, MD, Chief Medical Officer and Physician Lead for General Physician, PC, shared his group’s Vatica journey and the role accurate and complete coding and documentation play in helping close care gaps and deliver top-notch care.
Dr. Charles’ PCPs—like many—needed support on the risk adjustment journey. Dr. Charles and Vatica knew they needed to shift the group’s perceptions that risk adjustment is a benefit only for health insurers and engage the team purposefully in striving for accurate coding and documentation. “There’s been considerable education of our providers around risk assessment,” says Dr. Charles.
As providers continue to evolve their approaches and protocols in the name of value-based care, continued coaching and education around the upsides of improved risk adjustment—fair and accurate compensation, greater continuity of care, more proactive and higher-quality interactions and more—will separate the leaders from the pack.
“There’s been considerable education of our providers around risk assessment.”
— Richard Charles, MD, Chief Medical Officer and Physician Lead, General Physician, PC
Empowering teams to deliver quality care
Vatica provides clinical teams plus user-friendly technology at the point of care to enable PCPs at General Physician, PC to capture more accurate and complete diagnostic codes, which helps optimize risk adjustment and leads to accurate CMS reimbursement. A prospective program not only benefits health plans—it helps providers proactively manage care with a comprehensive pre-visit workup of all active and suspect conditions aggregated from various sources.
Curating only validated conditions and codes prior to the encounter, Vatica empowers PCPs to address HEDIS gaps through necessary interventions, like screenings or medication adherence, and make the most of their time with patients. “That pre-visit summary gets our providers thinking about not just the conditions but what care management is needed,” Dr. Charles explains. “It helps our providers build trust with patients.”
Vatica also provides group training, one-on-one education and CME courses to help PCPs and their teams understand and overcome the complexities of coding and capitalize on the benefits of better risk adjustment.
Closing gaps and opening doors
Dr. Charles cites a 10% improvement in risk score accuracy since General Physician, PC partnered with Vatica. He also found specific improvements in hemoglobin A1C levels and blood pressure control, attributed in part to Vatica’s process. “There’s a tremendous improvement in how many HEDIS gaps and how many other care gaps we’ve closed,” he says.
“There’s a tremendous improvement in how many HEDIS gaps and how many other care gaps we’ve closed.”
— Richard Charles, MD, Chief Medical Officer and Physician Lead, General Physician, PC
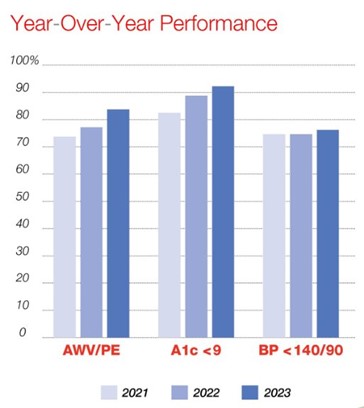
Figure 1: YoY Performance 2021–2023
General Physician, PC has capitalized on improved risk adjustment by using the newly captured revenue to offer additional services. These services give physicians valuable resources to help patients address issues and more time to focus on other clinical tasks and priorities. “We have a large clinical pharmacy program that addresses polypharmacy, high-risk drugs, transition of care, diabetes. We have nutrition, behavioral health, all of which are funded from these dollars,” explains Dr. Charles. “When a patient hears about all the services you have, they become more engaged.”
“We have a large clinical pharmacy program…nutrition, behavioral health, all of which are funded from these dollars.”
— Dr. Richard Charles, Chief Medical Officer and Physician Lead, General Physician, PC
Better coding in the name of better care
Accurate and complete coding benefits the provider, the practice and the patient. With Vatica as part of its risk adjustment protocol and clinic ecosystem, General Physician, PC has reduced the administrative burden on its team and optimized its diagnosis coding practices. And for Dr. Charles, that goes well beyond time savings or even compliance: “We want to take great care of these conditions, not just document that [patients] have them,” he concludes.










Recent Comments